Geothermal Engineering
Geothermal energy is natural heat extracted from the earth’s molten rock from underground. The temperature inside the earth is as high as 7,000 °C, but at depths of 80 to 100 km, the temperature drops to 650 °C to 1,200 °C. Geothermal energy can be classified according to the depth of burial as shallow geothermal (less than 400 m), medium geothermal (400 m to 1000 m), and deep geothermal (greater than 1000 m). For technical and cost reasons, shallow geothermal is more widely used, and can be subdivided into near-surface geothermal systems (no drilling required, usually within 4 m below the ground) and shallow geothermal borehole exchangers (less than 150 m at the bottom of the borehole).

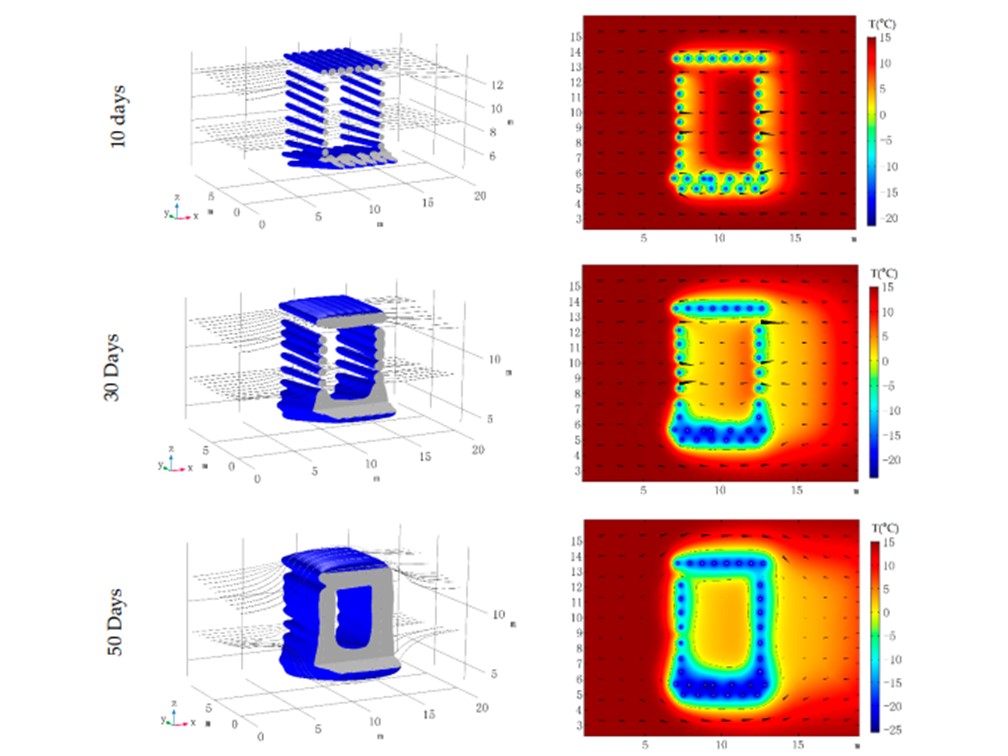
隧道冻结 (Tunnel Freezing)
地热能(geothermal energy)是从地下抽取的来自于地球内部熔岩的天然热能。地球内部的温度高达7000摄氏度,而在80至100公里的深度处,温度会降至650摄氏度至1200摄氏度。地热能根据埋藏深度可分为浅层地热(小于400米)、中层地热(400至1000米)以及深层地热(大于1000米)。由于技术和成本的原因,浅层地热的应用较广,其可细分为超浅层地热(无需钻孔,通常在地下4米以内产能)与浅层地热钻孔(钻孔底部小于150米)。
堤坝风险预测 (Dam risk prediction)
地热能(geothermal energy)是从地下抽取的来自于地球内部熔岩的天然热能。地球内部的温度高达7000摄氏度,而在80至100公里的深度处,温度会降至650摄氏度至1200摄氏度。地热能根据埋藏深度可分为浅层地热(小于400米)、中层地热(400至1000米)以及深层地热(大于1000米)。由于技术和成本的原因,浅层地热的应用较广,其可细分为超浅层地热(无需钻孔,通常在地下4米以内产能)与浅层地热钻孔(钻孔底部小于150米)。
